- HOME
- Products & Services
- Low Speed 4-stroke Diesel Engine
- Low-speed 4-stroke methanol-fueled engine
Methanol-Fueled Engine
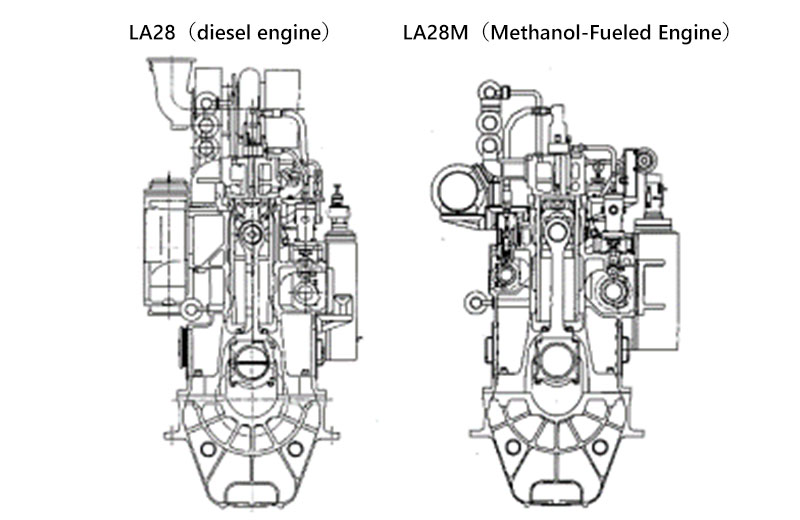
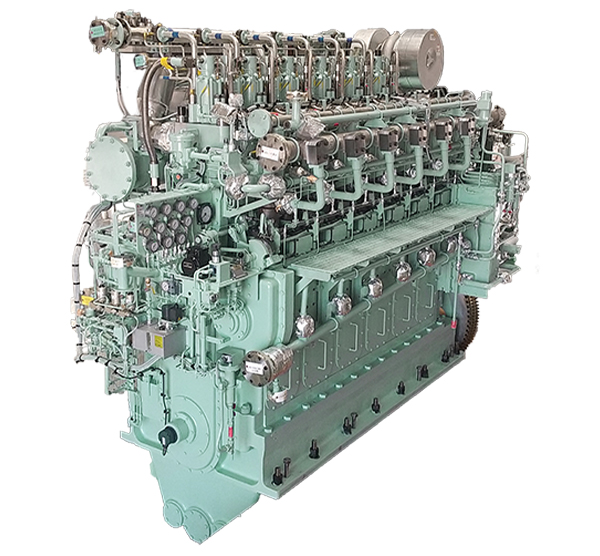
This direct injection-type methanol-fired diesel engine uses methanol as the main fuel and heavy oil A as the pilot fuel, and has the same basic structure as the existing low-speed 4-stroke diesel engine, which has earned a high level of trust from customers. This environmentally friendly engine produces less NOx, soot (PM), and sulfur oxides due to lower combustion temperatures compared to heavy oil.

Advantages
The methanol-fired engine is based on a proven low-speed 4-stroke diesel engine, using methanol as the main fuel and heavy oil A as the pilot fuel.
Except for the combustion injection system, the structure is the same as that of conventional engines, so reliability and durability are maintained.
Although the engine is a mono fuel combustion engine, even when the methanol supply is cut off, the ship can sail at the navigable speed prescribed by the classification using only pilot fuel (heavy oil A), thus ensuring redundancy.
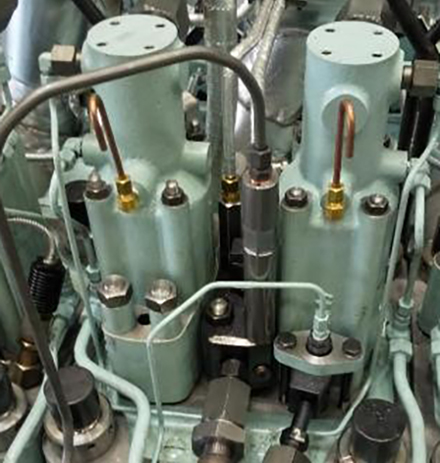
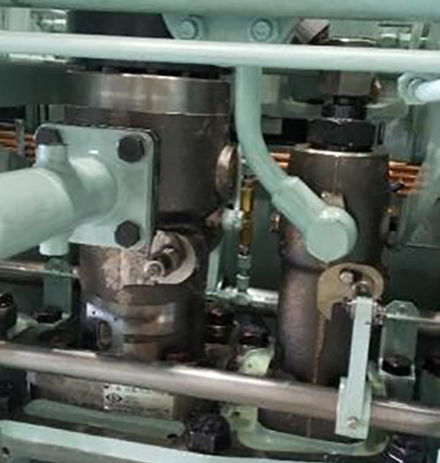


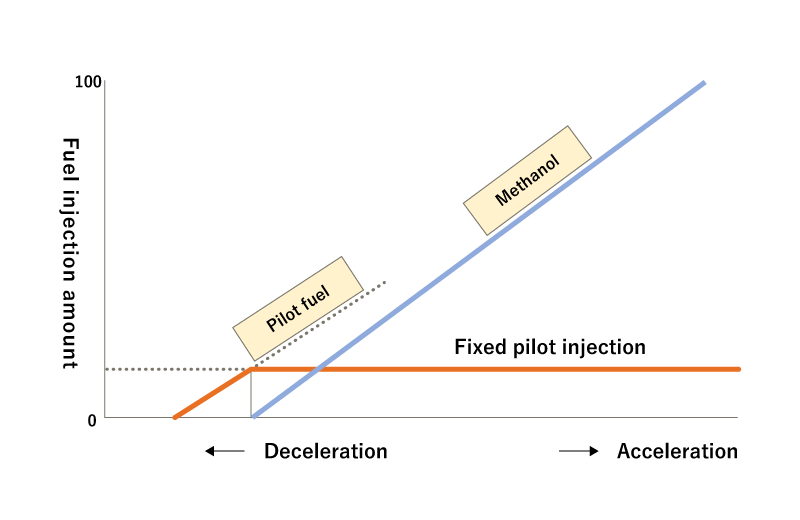
The main fuel injection valve for methanol and the pilot fuel injection valve are located in the cylinder cover, and the main fuel injection pump for methanol and the pilot fuel injection pump are located in the cam chamber and driven by the camshaft.

Methanol and pilot fuel injection is controlled by a proven hydraulic governor.
If there is an abnormality in the methanol supply system or if combustion failure occurs, the methanol is cut off, and the system switches to heavy oil A operation (40% load).
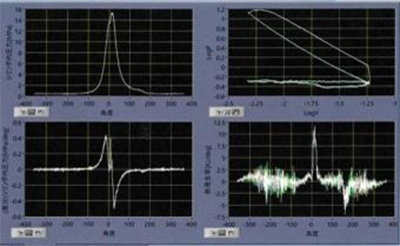
By constantly monitoring the pressure in the cylinder, the system can cut off the methanol and switch to heavy oil A operation in the event of abnormal combustion such as misfiring.
Methanol Fuel
Methanol is an environmentally friendly fuel that, when combusted, reduces sulfur oxide (SOx) emissions by up to 99%, soot (PM) emissions by up to 95%, nitrogen oxide (NOx) by up to 80%, and carbon dioxide (CO2 ) by up to 15%, in comparison with heavy oil, the main marine fuel used today. It is also relatively easy to store and handle because it remains in liquid form at room temperature and pressure.
Development background
As for methanol-fueled engines, a project was launched in 1988 by a group of government officials, related companies, and experts within the framework of the “Methanol Engine Promotion Committee” as part of a clean energy feasibility study. The LH28M, based on the LH28, the main engine of the time, was developed and tested, but was not shipped. This project never materialized after that, but with the recent increase in environmental awareness and reduction of GHG emissions, methanol is starting to attract attention as a fuel, and we are now in the process of developing a methanol-fueled engine conforming to the present-day rules, while following the technology of the time.
Difficulties during development
The LH28M methanol-fueled engine was developed more than 30 years ago, but the engineers who knew it back then have since retired, so we had to start over from scratch based on past data, which sometimes left us perplexed about this untested methanol-compatible technology.
Also, at that time, there were no regulations related to methanol for ships, and the LH28M designed at that time did not comply with current ship regulations. We went back and forth with the classification society to ensure compliance with the regulations, and repeatedly made changes to the design, which was the most labor-intensive and difficult part of the process.
Methanol-fueled engine introduction video
Particulars
Low-speed 4-stroke methanol-fueled engine
| Model | Number of cylinders | Output (kW) | Speed (min-1) | Cylinder bore (mm) | Stroke (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA28M | 6 | 1,103 | 330 | 280 | 590 |
Inquiries About Products
Please feel free to inquire with us on our products, services, or any other matters.